1.邻接矩阵
问题:
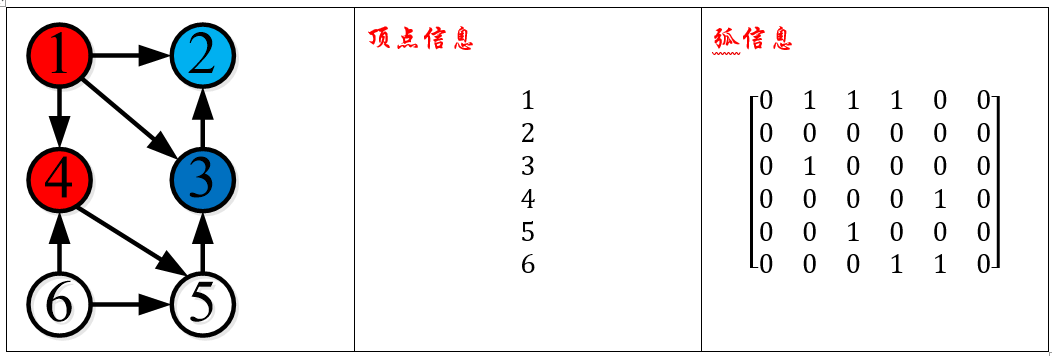
使用邻接矩阵存储方式建立有向图G。
1.1 数据准备
顶点数据:
vSet.txt1 2 3 4 5 6
弧数据:
arcSet.txt1 2 1 3 1 4 3 2 4 5 5 3 6 4 6 5
1.2 读取顶点信息
// 顶点信息从0开始存储,注意和矩阵映射 VertexType vexSet[MAX_VERTEX]; int vexLength = 0; FILE* fpVex = fopen("../data/vSet.txt", "r"); if (fpVex != NULL) { while (!feof(fpVex)) { fscanf(fpVex, "%d", &vexSet[vexLength]); vexLength++; } fclose(fpVex); }
1.3 读取弧信息
VertexType arcSet[MAX_VERTEX][2]; int arcSetLength = 0; FILE* fpArc = fopen("../data/arcSet.txt", "r"); if (fpArc != NULL) { VertexType srcVertex, dstVertex; while (!feof(fpArc)) { fscanf(fpArc, "%d %d", &srcVertex, &dstVertex); arcSet[arcSetLength][0] = srcVertex; arcSet[arcSetLength][1] = dstVertex; arcSetLength++; } fclose(fpArc); }
1.4 创建邻接矩阵存储有向图
// 创建一个基于邻接矩阵存储有向图 // vexSet: 一维数组,用于存储顶点信息 // arcSet: 二维数组,用于存储顶点之间的关系 // 如:一行(1,2):顶点1指向顶点2 // 注意:可将arcSet[][3]:分别存“顶点1指向顶点2,权值” bool createMGraph(MGraph* mG, GraphKind kind, VertexType vexSet[], int vexSetLength, VertexType arcSet[][2], int arcSetLength) { if (mG == NULL || vexSet == NULL || arcSet == NULL) return false; mG->kind = kind; // 存入顶点信息 mG->vexnum = vexSetLength; for (int i = 0; i < vexSetLength; i++) { mG->vexs[i] = vexSet[i]; } // 存入弧信息 mG->arcnum = arcSetLength; VertexType srcVertex = 0; // 弧尾 VertexType dstVertex = 0; // 弧头 // 初始化弧信息 //for (int row = 0; row < MAX_VERTEX; row++) // for (int col = 0; col < MAX_VERTEX; col++) // mG->arcs[row][col].weight = 0; // 将顶点数据存入弧中 for (int i = 0; i < arcSetLength; i++) { srcVertex = arcSet[i][0]; dstVertex = arcSet[i][1]; // ArcCell arcCell{ 1 }; mG->arcs[srcVertex - 1][dstVertex - 1].weight = 1; } return true; }
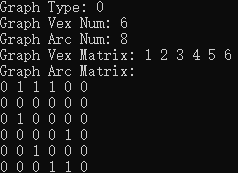
1.5 打印邻接矩阵图
void printMGraph(MGraph mG) { printf("Graph Type: %d\n", mG.kind); printf("Graph Vex Num: %d\n", mG.vexnum); printf("Graph Arc Num: %d\n", mG.arcnum); printf("Graph Vex Matrix: "); for (int i = 0; i < mG.vexnum; i++) { printf("%d ", mG.vexs[i]); } printf("\nGraph Arc Matrix: \n"); // 存储的顶点编号为0开始 for (int row = 0; row < mG.vexnum; row++) { for (int col = 0; col < mG.vexnum; col++) { printf("%d ", mG.arcs[row][col].weight); } printf("\n"); } }
运行结果:
2.邻接表
问题:
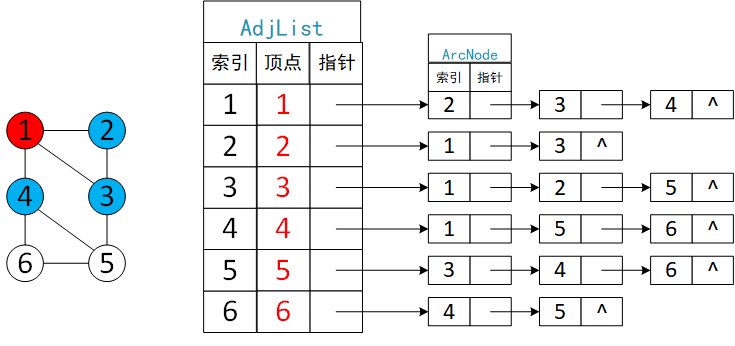
使用邻接表存储方式建立无向图G。
分析:
- 首先读入顶点信息,构建邻接数组之后,再读入弧信息。
- 然后再读入弧数据<两个顶点,两个顶点都能做源点,又能做终点,在两个头结点之后使用头插法插入弧结点>。
- 重复读取弧数据,生成弧结点插入,直到所有弧数据读完。
2.1 数据准备
2.2 读取顶点信息
2.3 读取弧信息
2.4 创建邻接表存储无向图
- 首先读入顶点信息,构建邻接数组之后,再读入弧信息。
- 然后再读入弧数据<两个顶点,两个顶点都能做源点,又能做终点,在两个头结点之后使用头插法插入弧结点>。
- 重复读取弧数据,生成弧结点插入,直到所有弧数据读完。
// 创建一个基于邻接表存储无向图 // vexSet: 一维数组,用于存储顶点信息 // arcSet: 二维数组,用于存储顶点之间的关系 // 如:一行(1,2):顶点1指向顶点2 // 注意:可将arcSet[][3]:分别存“顶点1指向顶点2,权值” bool createALGraph(ALGraph* G, GraphKind kind, VertexType vexSet[], int vexSetLength, VertexType arcSet[][2], int arcSetLength) { if (G == NULL || vexSet == NULL || arcSet == NULL) return false; G->kind = kind; // 构造邻接数组vertice,每个元素包括顶点信息和头结点指针 // 每次从vexSet中读入一个元素(顶点的信息) for (int i = 0; i < vexSetLength; i++) { VertexType vertex = vexSet[i]; // 注意:顶点编号和索引一一对应 // 将顶点信息存入头结点 G->vertices[vertex].data = vertex; // 注意头结点指针赋空,方便后序头插 G->vertices[vertex].first = NULL; } // 开始在边表中插入顶点,使用头插法 VertexType srcVertex = 0; // 源点 VertexType dstVertex = 0; // 终点 for (int j = 0; j < arcSetLength; j++) { srcVertex = arcSet[j][0]; // 源点 dstVertex = arcSet[j][1]; // 终点 // 生成一个包含dstVertex弧结点,插入到srcVertex头节点中 ArcNode* arcNodePtr = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); arcNodePtr->adjvex = dstVertex; arcNodePtr->weight = 0; // 头插法插入到头结点 arcNodePtr->next = G->vertices[srcVertex].first; G->vertices[srcVertex].first = arcNodePtr; // 生成一个包含srcVertex弧结点,插入到dstVertex头节点中 arcNodePtr = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); arcNodePtr->adjvex = srcVertex; arcNodePtr->weight = 0; // 头插法插入到头结点 arcNodePtr->next = G->vertices[dstVertex].first; G->vertices[dstVertex].first = arcNodePtr; } // 设置顶点,弧数量 G->vexnum = vexSetLength; G->arcnum = 2 * arcSetLength; return true; }
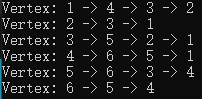
2.5 打印邻接矩阵图
void printALGraph(ALGraph G) { for (int i = 1; i <= G.vexnum; i++) { ArcNode* pNextNode = G.vertices[i].first; printf("Head: %d ", G.vertices[i].data); VertexType src = G.vertices[i].data; //头节点 while (pNextNode != NULL) { // printf("%d ---> %d\n", src, pNextNode->adjvex); printf("-> %d ", pNextNode->adjvex); pNextNode = pNextNode->next; } printf("\n"); } }
运行结果